 (rollover to compare with normal)
(rollover to compare with normal) |
|
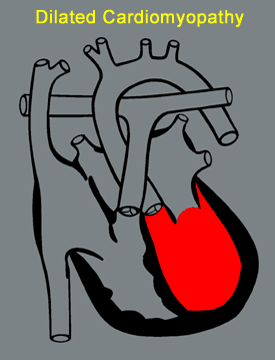
What Are Its Effects And Treatment?
The effects of Dilated Cardiomyopathy vary in seriousness depending on the degree of heart muscle weakness and dilation. Fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath are commonly experienced with physical exertion. There may also be difficulty breathing while lying down (orthopnea). There is a characteristic heart murmur and water retention (edema) of the legs is a frequently associated symptom. In some cases, there can be an improvement in the heart's performance over time.
Mildly affected individuals may require no treatment. For patients with symptoms and significant heart dysfunction, medications may be prescribed as an outpatient to preserve heart function lowering the blood pressure in the arteries (after load reduction, ACE inhibitor, eg Linsinopril ®) and to slow the heart rate (beta blocker, eg Carvedilol ®). If heart function continues to deteriorate, medication to strengthen the pumping action of the heart (Inotropes, Milrinone ®). This makes it easier for the left ventricle to do its job of pumping blood to the body tissues.
Water pills (diuretics) may also be helpful in reducing the fluid retention.
In cases where the weakness of the heart muscle is severe and progressive, a heart transplant may be necessary and a ventricular assist device used to bridge to transplant. |